
From my point of view, RESTful web service is light weight web service and very flexible if you compare with SOAP web service. But the cons of the RESTful web service is the communication format is specify in certain format when you compare to the SOAP Web Service. In this post we will create and apply secure scheme as we have use for JAX-WS (SSL/HTTPS, user and password) to secure our RESTful web service. Java EE provide very ease to create RESTful Web service.
Create RESTful web service.
First, you need to create Dynamic Web Project by using eclipse. I call this project as java-ee-02-jaxrs. |
| Create Dynamic web Project |
 |
| Select source folder |
 |
| Finish |
 |
| Add Dependency Project |
sid varchar primary key,
title varchar not null,
author varchar not null
);
Next is to create JPA Entity from table
 |
| Create JPA Entity from Table |
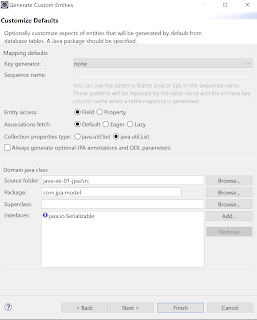 |
| Click Next |
 |
| Click Finish |
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.persistence.*;
/**
* The persistent class for the booktbl database table.
*
*/
@Entity
@Table(name="booktbl")
@NamedQueries({
@NamedQuery(name="Book.findAll", query="SELECT b FROM Book b"),
@NamedQuery(name="Book.findBook", query="SELECT b FROM Book b where b.sid = :sid")
})
public class Book implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Id
@Column(name="sid")
private String sid;
@Column(name="title")
private String title;
@Column(name="author")
private String author;
public Book() {
}
public String getAuthor() {
return this.author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
public String getTitle() {
return this.title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title= title;
}
public String getSid() {
return this.sid;
}
public void setSid(String sid) {
this.sid = sid;
}
}
Next in the EJB project, you just create business logic class BookEjb.class as below.
import java.util.List;
import javax.ejb.LocalBean;
import javax.ejb.Stateless;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.persistence.PersistenceContext;
import javax.persistence.Query;
import com.jpa.model.Book;
/**
* Session Bean implementation class BookEjb
*/
@Stateless(mappedName = "bookEjb")
@LocalBean
public class BookEjb {
/**
* Default constructor.
*/
@PersistenceContext(name="java-ee-01-jpa")
private EntityManager em;
public BookEjb() {
super();
}
public void save(Book book) {
em.persist(book);
}
public List<Book> getBooks(){
Query query = em.createNamedQuery("Book.findAll");
return query.getResultList();
}
public Book getBook(String sid) {
Query query = em.createNamedQuery("Book.findBook", Book.class);
query.setParameter("sid", sid);
return (Book) query.getSingleResult();
}
}
import javax.ws.rs.ApplicationPath;
import javax.ws.rs.core.Application;
@ApplicationPath("/api")
public class EndPointApplication extends Application {
public EndPointApplication() {
super();
}
}
import java.util.List;
import javax.annotation.security.RolesAllowed;
import javax.ws.rs.Consumes;
import javax.ws.rs.GET;
import javax.ws.rs.POST;
import javax.ws.rs.Path;
import javax.ws.rs.PathParam;
import javax.ws.rs.Produces;
import javax.ws.rs.core.MediaType;
import com.jpa.model.Book;
@Path("/book")
@RolesAllowed("webservice")
public interface BookCrud {
@Path("/save")
@POST
@Consumes(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
public void save(Book book);
@Path("/list")
@GET @Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
public List<Book> getBooks();
@Path("/get/{sid}")
@GET @Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
public Book getBook(@PathParam("sid")String sid);
}
Finally, you can create class that implement the interface.
import java.util.List;
import javax.ejb.EJB;
import javax.enterprise.context.RequestScoped;
import javax.inject.Named;
import com.ejb.crud.BookEjb;
import com.jpa.model.Book;
@Named
@RequestScoped
public class BookCrudImp implements BookCrud {
@EJB
private BookEjb bookEjb;
@Override
public void save(Book book) {
bookEjb.save(book);
}
@Override
public List<Book> getBooks() {
return bookEjb.getBooks();
}
@Override
public Book getBook(String sid) {
return bookEjb.getBook(sid);
}
}
In order to allow client (on others machines) to be able to use those service, we need to create one more class to allow cross-origin access as below.
package pro.itstikk.wildfly;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.ws.rs.container.ContainerRequestContext;
import javax.ws.rs.container.ContainerResponseContext;
import javax.ws.rs.container.ContainerResponseFilter;
import javax.ws.rs.ext.Provider;
@Provider
public class CORSFilter implements ContainerResponseFilter {
@Override
public void filter(final ContainerRequestContext requestContext,
final ContainerResponseContext cres) throws IOException {
cres.getHeaders().add("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "*");
cres.getHeaders().add("Access-Control-Allow-Headers", "origin, content-type, accept, authorization");
cres.getHeaders().add("Access-Control-Allow-Credentials", "true");
cres.getHeaders().add("Access-Control-Allow-Methods", "GET, POST");
cres.getHeaders().add("Access-Control-Max-Age", "1209600");
}
}
Next is to setup HTTPS and enable Basic Authentication through your web.xml and creat jboss-web.xml, you can refer here for securing web service. After finish, you can restart your wildfly and test.
 |
| Project Structure |
For testing, you can use POSTMAN and add Basic Authentication.
 |
| Set Up Basic Authentication |
 |
| Test Post Request |
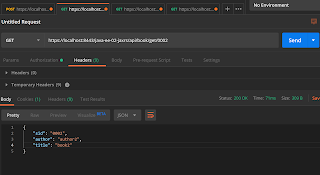 |
| Test GET Request 01 |
 |
| Test GET Request 02 |
Reference
- Using Wildfly Create JAX-RS 01
- Create JAX-RS Web Service Tutorial
- How to enable Cross domain requests on JAX-RS web services
No comments:
Post a Comment